Prospecting in Sales – What It Is and How It Works

Every sales rep knows the feeling: a new quarter begins, fresh sales targets are set, and the contact list has already shrunk. That’s when prospecting takes center stage—one of the most critical elements of a salesperson’s job. In other words, it’s the process of finding potential buyers who don’t yet know your offer but could become a valuable part of your pipeline.
Prospecting in sales isn’t about randomly sending messages, blasting cold calls, or dialing numbers without a plan. It’s a thoughtful, systematic approach often referred to as the sales prospecting process. The goal is to ensure every lead is properly identified, turned into qualified leads, and prepared for a meaningful conversation with a sales rep.
In practice, prospecting means building a bridge between prospective customers and existing customers who already benefit from your product or service. With well-executed sales prospecting efforts, reps can move smoothly from identifying prospects to initiating the first conversation, and ultimately to advancing them through the sales cycle.
Why Prospecting Is the Foundation of Effective Sales
Whether you’re selling SaaS software, industrial machinery, or professional consulting services—prospecting is the cornerstone of the sales process. Without it, sales reps have no one to talk to, and opportunities simply don’t appear in the pipeline.
Companies that treat sales prospecting as a key strategic activity achieve far better results in the long run. Why? Because they don’t sit back and wait for new clients to show up. Instead, they proactively build a list of qualified leads that match their buyer persona. This, in turn, allows sales teams to plan their pipeline more effectively, forecast revenue with greater accuracy, and tailor the offer to the actual needs uncovered during the buying process.
Prospecting also creates a major advantage in relationship-building. While competitors rely on luck, companies with a structured sales strategy already have a segmented list of target accounts aligned with market needs. To achieve this, modern sales teams combine traditional methods like phone calls and direct mail with digital tactics such as LinkedIn outreach, social media platforms, and AI-powered prospecting tools.
In short—successful prospecting is the practice that turns strangers into real business conversations. It’s the first step toward maintaining a healthy customer base, developing long-term relationships, and consistently driving new revenue.

What Exactly Is Prospecting?
Put simply, prospecting is the systematic search for prospective buyers who may be interested in your offer. It’s the starting point that allows a company to “open doors” to new business relationships and initiate contact with potential clients.
In practice, prospecting is about deliberately identifying people or companies that meet specific criteria—such as company size, industry, industry trends, or customer needs. It’s not about random contacts but about using proven sales prospecting techniques and structured sales prospecting methods to reach the right audience.
For example, a rep selling SaaS software might focus on target companies in fast-growing industries, while a manufacturing rep may prioritize organizations expanding their production lines. The key is to connect with people who not only fit the buyer persona but also show genuine interest in solving their challenges.
Effective prospecting also requires understanding the prospect’s business—their goals, budgets, and the prospect’s pain points. By doing so, sales reps avoid wasting time on irrelevant conversations and instead focus on higher quality leads. Importantly, prospecting doesn’t end with collecting contact information. It also involves crafting a compelling sales pitch, establishing initial contact, and laying the foundation for long-term relationships that turn leads and prospects into satisfied customers.
That’s why sales prospecting important—it’s a core building block of every sales process. It’s the starting line of the journey that leads to acquiring new customers, building trust, and scaling the business.
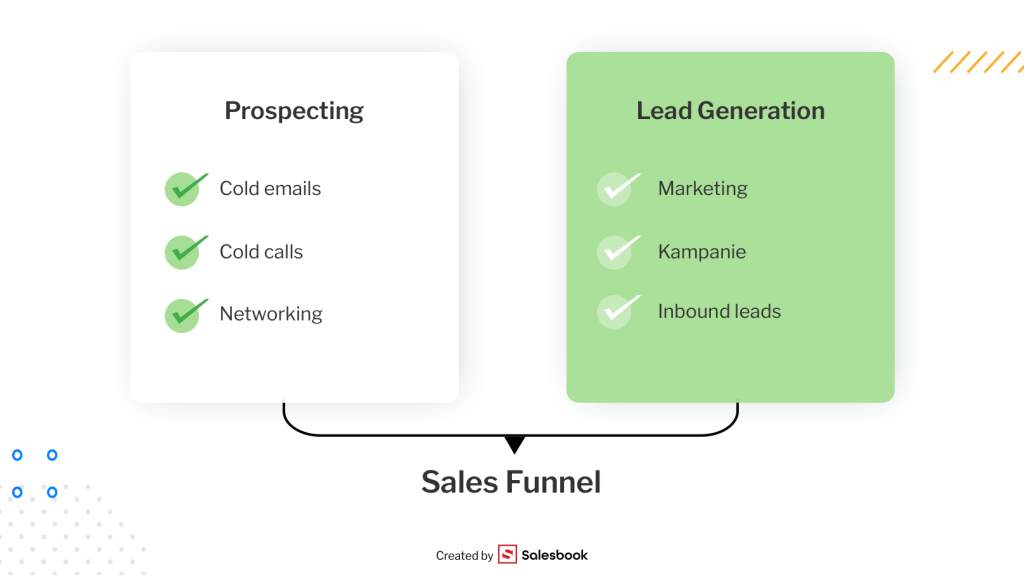
Prospecting vs. Lead Generation – Similarities and Differences
At first glance, sales prospecting and lead generation might seem similar. Both aim to fill the sales funnel with potential leads. However, the approaches differ.
Outbound prospecting is an active effort carried out by sales reps—sending cold emails, making cold calls, attending networking events, or reaching out through social media platforms. Here, the rep identifies and initiates the first interaction with prospects, often guided by own research and clear prospecting strategies.
Inbound prospecting, by contrast, is more passive and usually driven by marketing. Think campaigns, content marketing, digital ads, or website forms. In this case, inbound leads voluntarily share their contact details, and it’s up to sales teams or account executives to qualify them afterward.
The similarity lies in the outcome: both approaches deliver contacts to the sales funnel. The difference is how those contacts arrive.
In practice, the most effective prospecting strategies come from combining both. Outbound strategies allow sales reps to reach key decision makers in strategic target accounts quickly, while inbound marketing campaigns attract prospects at scale and provide valuable customer data. Together, they form a powerful mix: direct outreach (like cold emails, direct mail, or meetings) reinforced by inbound marketing that builds credibility and attracts prospective customers.
This synergy is what keeps the sales pipeline steady and ensures the business doesn’t rely on a single source of contacts. It also gives sales reps valuable insights into what buyers prefer and how to align outreach with the modern buying process.
The Prospecting Process Step by Step
Although sales prospecting may sound complex, it’s essentially a series of repeatable steps that every rep should master. In a well-structured prospecting process, it’s not just about collecting new contacts—it’s about selecting and preparing them for the next stages of the sales cycle.
Prospecting activities can be broken down into three main stages: identification, building the database, and qualification. Each step has a huge impact on the final sales results and overall team performance.
Identifying a Potential Customer
The first step is defining who your potential customer really is. It’s not about random people, but those who fit a clearly defined target profile.
At this stage, data-driven prospecting is crucial—using both internal data (CRM, current customers) and external sources (business databases, industry tools, social media). A sales rep needs to understand where the ideal customers are and how to reach them.
This involves gathering information about industry, company size, and even customer preferences. Proper identification allows you to choose the right outreach techniques later—whether that’s face-to-face meetings, cold emails, or social selling.
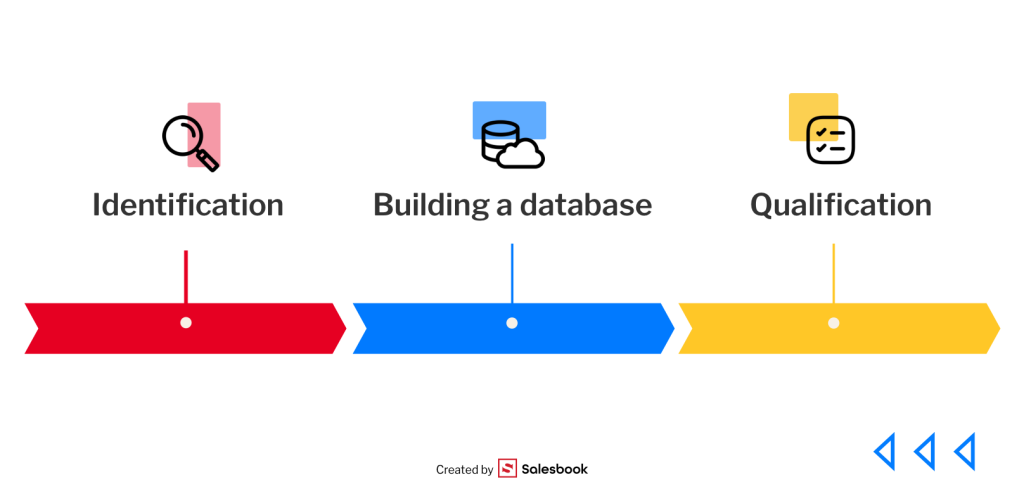
Building a Database of Potential Customers
Once you know who your potential customer is, the next step is creating a consistent list of contacts. Building a database of prospects means gathering all the information in one place—most often in a CRM system.
It’s important not to confuse quantity with quality. Simply dumping hundreds of unverified email addresses into a database won’t bring results. Precision matters. That’s why it’s better to have 50 well-matched prospects than 500 random contacts who will never make a purchase.
Prospecting at this stage includes both manual data collection and the use of automation tools. This way, the sales rep can be sure that the contact list is accurate, segmented, and ready for outreach.
Verifying and Qualifying New Prospects
The final step is determining which of the contacts in your database actually have the potential to become customers. This is where the sales rep evaluates whether a company or individual fits the ideal customer profile and is worth the time investment.
Introductory calls, in-person meetings, or even quick cold emails can help in this stage. The goal is to confirm that you’re dealing with the right prospect who could eventually lead to a signed deal.
A well-run qualification process saves time—ensuring reps don’t waste energy on contacts that will never convert, but instead focus on real opportunities.
Prospecting Techniques That Work
Prospecting isn’t random. It’s a set of specific tools and methods that help salespeople reach the right prospects. Each technique should be tailored to the industry, product type, and customer preferences. Without that, effectiveness and deal closure become unlikely.
Here are three methods that are most commonly used in practice—and consistently deliver results.
Cold Emailing – How to Write Messages That Actually Get Replies
A well-crafted cold email is one of the most effective prospecting tools. It’s about sending messages to people who have never interacted with your company before. To avoid ending up in the trash folder, personalization and clarity are key.
The message should be short, specific, and address real needs. A sales rep shouldn’t start by describing the product, but by showing an understanding of the problem the prospect is facing. Only then does it make sense to suggest a meeting or a quick call.
It’s also a best practice to test different versions of your emails. This helps identify which elements grab attention and increase the chances of a response.
Social Selling and Building a Sales Rep’s Personal Brand
The second technique is social selling—using social media to build relationships with prospects. The goal here isn’t direct selling, but consistently building an expert image.
A sales rep who publishes valuable content, joins discussions, and demonstrates industry knowledge naturally becomes a credible partner for conversation. This makes outreach more organic—prospects start showing interest in your offering on their own.
Social selling works best as a complement to cold emailing. If you send a message and the recipient later sees you actively engaging on LinkedIn, your credibility and chances of a reply grow significantly.
Networking and Industry Events
There’s no substitute for face-to-face interaction. That’s why networking and attending industry events remain among the most valuable prospecting methods. Personal conversations help build trust faster and uncover real challenges on the other side.
Meeting in person often shortens the path from the first conversation to closing a deal. Plus, it creates opportunities not only with potential customers but also with business partners and industry thought leaders.
It’s crucial to remember that networking doesn’t end when the trade show or conference does. The follow-up is key—a thank-you email, a LinkedIn connection request, or scheduling a next meeting. These actions are what ultimately lead to a lasting client base.
Tools That Support Prospecting
Modern sales teams no longer rely on sticky notes or Excel spreadsheets. Effective prospecting requires the right tech stack that enables smooth management of prospects, activity tracking, and performance measurement. For sales professionals, the right tools are the difference between wasted time and a consistent flow of qualified leads.
Well-chosen technology not only streamlines the sales process but also provides valuable insights into the prospect’s journey. Tools like LinkedIn Sales Navigator, Apollo.io, and Salesbook’s AI-powered CRMhave become standard for modern sales teams because they make it easier to find prospects, segment them, and design more effective prospecting strategies.
These tools help sellers understand customer data, track responses, and evaluate which sales prospecting methods deliver the best results. In many cases, they also integrate with marketing materials and automation platforms, so sales and marketing work hand in hand to nurture leads.
CRM as the Sales Rep’s Command Center
A CRM system is the modern salesperson’s mission control. It holds all prospect information, contact history, and deal data in one place. This means sales reps no longer need to rely on memory or scattered notes—everything is accessible, structured, and always up to date.
More importantly, modern CRMs allow segmentation by industry, company size, or customer preferences. That’s a huge advantage, as it enables reps to personalize their outreach and tailor their sales pitch to each prospect’s pain points.
This level of personalization is one of the most effective prospecting strategies available today. For example, a rep using LinkedIn Sales Navigator inside their CRM can filter target companies by location, size, or recent industry trends, and then sync those contacts directly into their pipeline. Instead of chasing cold leads, the sales rep can prioritize accounts with genuine interest and a higher likelihood of conversion.
This makes outreach far more effective. Reps can see who opened an email, when the last initial contact happened, and what was agreed upon during previous conversations. For managers, it creates a transparent view of the sales prospecting process, showing which key tactics work and where the team needs support.
It’s not just convenience—it’s the system that often determines whether sales prospecting efforts result in successful outreach or get lost in the noise of everyday activity.
AI-Powered Prospecting Automation
The second pillar of modern prospecting is artificial intelligence. Automation not only speeds up outreach but also ensures messaging is better aligned with market expectations. For modern sales teams, AI has become a game-changer in the prospecting game.
AI makes it possible to analyze massive datasets and identify which prospects are most likely to respond. Instead of guessing, reps can see exactly which accounts show signs of interest and which are simply unqualified leads. Algorithms can even suggest the best time to send a message, how to personalize it, and which social media channels or outreach tactics will have the biggest impact.
This elevates both outbound prospecting and inbound prospecting efforts. Outbound activities such as cold calls, direct mail, or targeted email campaigns become more efficient when AI indicates which sales prospecting techniques will resonate most with a given buyer persona. On the inbound side, automation ensures that inbound leads are scored and prioritized quickly, helping reps focus only on the most relevant opportunities.
In practice, this means reps don’t have to operate blindly. Instead of a “spray and pray” approach, they receive actionable recommendations: who to contact, when, and how. This doesn’t just increase efficiency—it produces higher quality leads and dramatically improves conversion rates.
By removing repetitive work from the sales prospecting process, AI frees sales reps to concentrate on more strategic tasks: nurturing existing customers, preparing a personalized sales pitch, or building stronger relationships with key decision makers.
Common Prospecting Mistakes—and How to Avoid Them
Prospecting is a process where mistakes often repeat themselves. Sometimes it’s because of pressure to deliver results; other times, it’s due to the lack of a clear strategy. The most common pitfalls include:
No segmentation
Throwing every contact into the database regardless of profile wastes time and weakens results. Instead of prioritizing potential prospects who match your buyer persona, reps get lost chasing irrelevant accounts.
Being too pushy
Bombarding prospects with cold calls, emails, and LinkedIn messages without first understanding the prospect’s pain points. Effective selling isn’t just a pitch—it’s about solving problems.
Skipping follow-ups
One message is rarely enough. Without persistence and proper sequencing, many opportunities slip away. Successful reps know that contacting potential customers multiple times with personalized, value-driven outreach is essential.
Poor use of tools
CRM systems, AI-driven scoring, and data enrichment platforms can deliver valuable insights, but if configured poorly, they create chaos instead of clarity.
Focusing only on quantity
Sending thousands of emails or chasing too many cold leads may look like productivity, but the real goal is generating higher quality leads that move through the sales cycle.
Avoiding these mistakes requires discipline, structured prospecting strategies, and proper training. The best reps do their own research before outreach, tailor their sales pitch to each prospect’s business, and nurture relationships over time.
Ultimately, treating prospecting as an investment—not just a quick fix for an empty pipeline—is what separates those who burn out from those who build a successful career in sales.
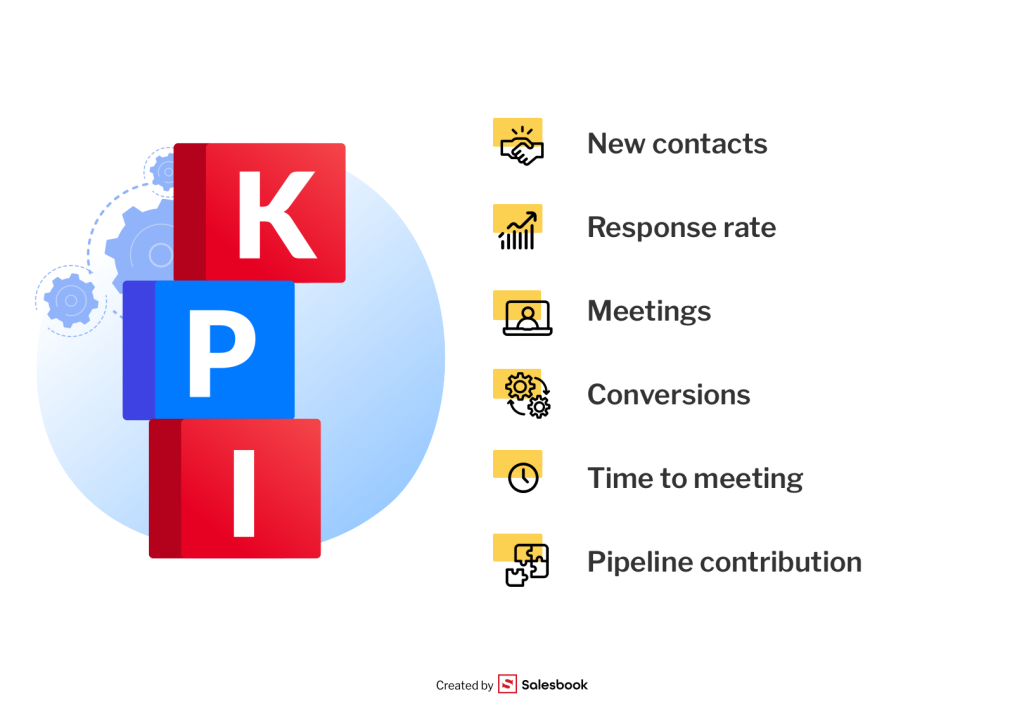
How to Measure Prospecting Success
Without tracking results, no sales activity makes sense. In prospecting, a few key metrics should always be monitored. These metrics not only show progress but also provide valuable insights into which prospecting strategies drive results and which need improvement.
- Number of new contacts – how many prospects were added to the database in a given period. A growing list of potential prospects indicates healthy activity, but the focus should remain on quality, not just volume.
- Response rate – what percentage of messages (e.g., cold emails or direct mail) receive a reply. A low response rate may signal that your sales pitch isn’t aligned with the prospect’s pain points.
- Number of meetings – how many prospects advanced to an actual conversation. This is one of the clearest indicators of successful outreach.
- Conversion to next stages – how many moved from initial contact to proposal stage. High conversion means your key tactics are resonating with the right audience and generating qualified leads.
- Time to meeting – how quickly prospects move from the first interaction to a scheduled call. Shorter timelines usually reflect well-structured follow-ups and effective prospecting strategies.
- Pipeline contribution – how much of the sales pipeline is generated directly from prospecting efforts. Top-performing reps often use a mix of outbound prospecting and inbound prospecting to balance results.
For sales teams, monitoring these KPIs is one of the most effective prospecting strategies. It allows both reps and managers to quickly assess which channels (e.g., social media platforms, phone calls, attending networking events) are working and which require optimization.
As a rule of thumb, one of the best sales prospecting tips is to track metrics consistently over time, not just at the end of a quarter. This ongoing feedback loop makes it easier to refine your prospecting game, double down on what works, and eliminate wasted effort.
In short, measurement transforms prospecting from guesswork into a science—and that’s how modern sales teams achieve predictable growth.
Conclusion – Prospecting as the Path to Long-Term Relationships
Prospecting isn’t just about quickly “opening doors” to new conversations. It’s the foundation for building a company that grows in a stable and predictable way. A well-structured sales prospecting framework ensures that sales reps don’t face the pressure of an empty contact list, and managers gain full control of the sales process.
Properly executed sales prospecting creates something much more valuable than a list of numbers in a CRM—it builds a network of meaningful relationships with potential buyers and existing clients alike. These relationships become the backbone of predictable revenue growth, helping companies weather market shifts while steadily moving prospects through the sales cycle.
For sales reps, the best time to start prospecting is always now. Top performers know that consistency matters: staying disciplined with daily outreach ensures a full pipeline and better long-term results. And when sellers early enter the conversation—identifying needs before competitors do—they gain an unbeatable advantage.
In the end, prospecting is more than just filling the funnel. It’s about creating long-term trust and partnerships that drive revenue and ensure business sustainability. That’s why companies that invest in effective prospecting strategies consistently outperform their peers and secure leadership positions in their markets.
Want to see how a CRM system can supercharge your sales prospecting efforts? Book a free live demo with one of our experts.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions
What is sales prospecting?
Sales prospecting is the active search for potential buyers and introducing them into the sales funnel. It’s the first step to building long-term relationships and driving predictable revenue growth.
How does prospecting differ from lead generation?
Lead generation relies on marketing to encourage prospects to leave their data. Prospecting is active—the sales rep or account executives take the initiative and reach out directly to the right people.
What are the most effective prospecting techniques?
The most common are cold emailing, social selling, and networking at industry events. The best results come from combining them with a structured sales process that ensures consistency. In many cases, success comes when sellers early identify opportunities and engage before competitors.
What tools support prospecting?
The essentials include CRM systems, which organize customer data, and AI-powered solutions, which automate and personalize outreach. Tools like LinkedIn Sales Navigator, Apollo.io, or Salesbook CRM also help reps find prospects and track performance.
How long does the prospecting process take?
It depends on the industry and type of customer. In B2B sales, sales prospecting can take weeks—or even months—before reaching the first meeting or closing a deal. What matters most is consistency: the sooner you start prospecting, the faster you build a predictable pipeline of qualified leads.
Table of Contents







