

Sales

4 May 2023
Sales analysis allows you to perceive the entire sales process from a distance. However, are key performance indicators enough to see the full perspective of the work of a sales team? What else can you add to your sales reports to make your analysis effective? How to increase average revenue based on sales data?
Sales analysis is a process that relies on gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data on selling products or services. During analysis, you should include different factors that cause an increase or a decrease in sales. Therefore, reading reports can be very helpful.
Data included in reports come from various areas. They show, for example, the average sales cycle length, sales performance in relation to the given time, customer acquisition costs, customer lifetime value (CLV), number of complaints, number of new customers, and many more.
As David Sides said,
“Data is like dim light when you get lost in a dark room. Follow it, try to understand it, and maybe you will actually know where you are and what is around you.”
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are used by sales managers and high-performing sales teams to maximize profits, be successful, beat their competitors, and boost sales revenue.
It is important to track sales KPIs because they show a given company’s development and the progress of its employees. KPIs measure sales efforts, we can say that they change hard data into sales metrics that help you to check if your business is able to achieve essential goals.
Every company that has its sales strategy uses sales performance metrics to know which elements in the sales process need improvement and which are profitable.
The definition of sales KPIs says that they should be SMART: specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-based.
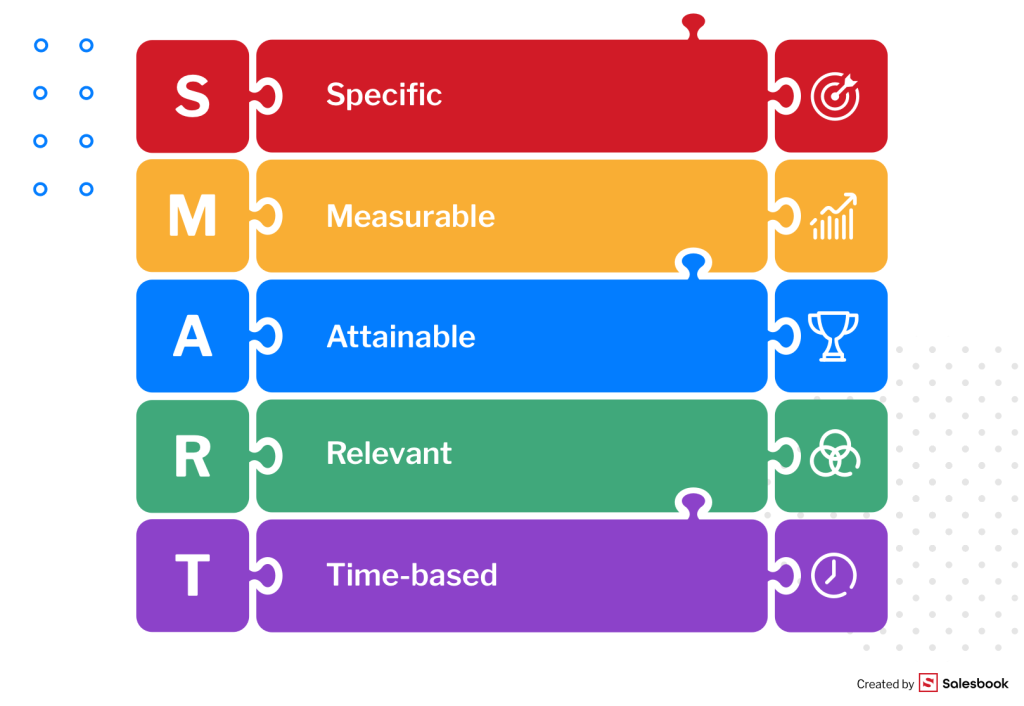
However, there are no universal KPIs for every business. Metrics depend on the type of company and industry.
For example, in e-commerce, it is important to track the average purchase value, the number of complaints in an e-shop, or the conversion rate. Marketing teams will track the average customer acquisition cost, lead conversion rate, and customer lifetime value (CLV). The last metric shows the entire revenue your business can expect from a customer.
Obviously, your sales team has to analyze KPIs. It depends on your company and your decision on which sales KPIs will be important for your sales reps. What are the best KPIs for sales?
You need to consider even historical sales data to know what affected sales growth; thanks to that, you can perceive repetitive patterns; you can find such sales data inside your company in sales reports.
Sales metrics needed in this analysis are related to the costs of sales (marketing, production, research of customer satisfaction, market analysis).
This analysis contains information about the number and value of sales transactions and gross profit.

This analysis shows which products or services are the most popular among existing customers and new clients, this can also show which customer segments are profitable and how much revenue they bring to the company, thanks to this analysis, a given sales rep knows which goods and customers are worth focusing on.
This analysis shows which customers continue to buy your products or services and why.
Sales KPI included in this analysis tracks the costs of acquiring new customers (both in sales and marketing), if you understand the results of this analysis you will be aware of which resources of leads increase your profit (cost per lead).
You can track and analyze the work of the entire sales team or a chosen sales rep. Moreover, you can compare an individual rep performance metrics with a contact method, and the number of follow-up e-mails or meetings. Thanks to this, you can have a bigger picture of the work of your sales department.

If you analyze a sales funnel you know which behaviors of your customers are repetitive, and what kind of sales activities are effective, this knowledge allows you to improve some elements of a sales pipeline to sell more.
Thanks to this analysis, you know which sales reps are the most effective and what kind of method they use to be persuasive in a sales process.
It is an analysis of a strategy from a short and long-time perspective, you need it to plan your budget, for example, each customer may have an estimated purchase value.
These are examples of analyses that you can do in your company. Each analysis will require a different sales KPI to be completed. Of course, you add more metrics important to track, such as monthly recurring revenue, monthly sales growth, cost per lead, and the number of qualified leads.
However, there are opinions that companies do not need a lot of KPIs. They just need the right sales KPIs.
Regardless of the analysis and sales KPIs you choose, you need hard data to have a realistic picture of how your company works. Lack of reliable data leads to combining analysis with hypothesis. Meanwhile, the success and effectiveness of sales leaders who work for you, depend on how you interpret data. Interpreting data affects redefining sales KPIs, sales strategies, or even methods applied by sales reps.
There are numerous arguments to support the thesis that every company should not neglect sales analysis and reliable data.
An iceberg is the best metaphor that represents the results of gathering incomplete data on sales activities. What is the hidden meaning? If you see an iceberg in the sea, you usually perceive only its tip. However, you do not know what is under the surface of the water. A large part of the iceberg can be hidden.
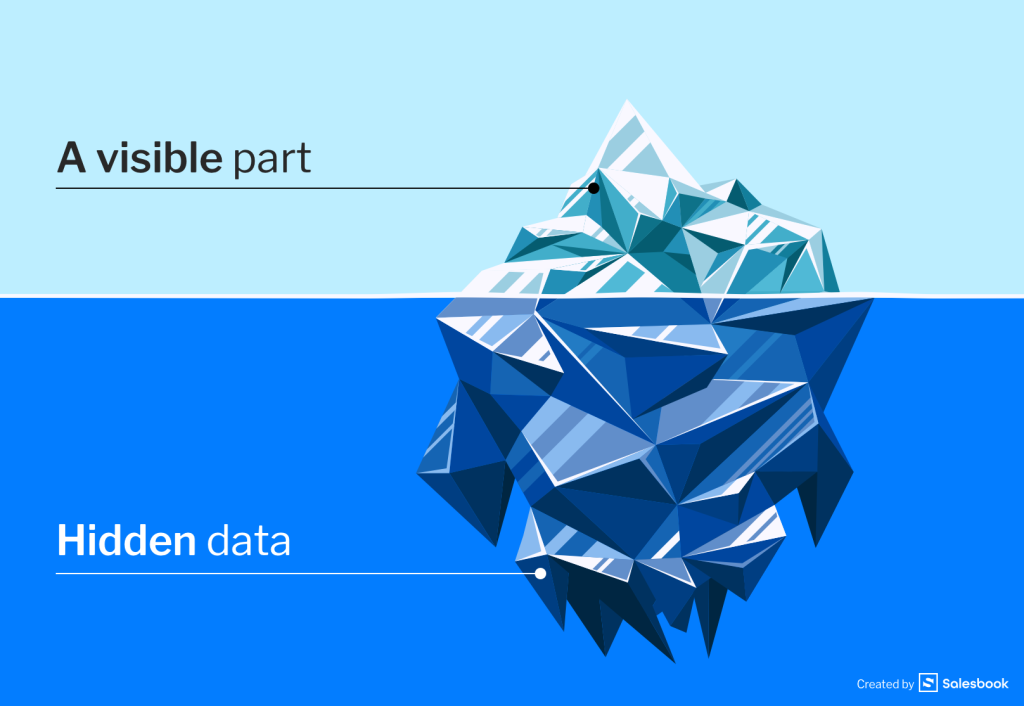
The tip of the iceberg theory is widely known in psychology because of Sigmund Freud. He was of the opinion that the tip is our conscious knowledge, and the unaware part is under the water.
This theory can be related to the sales process. Sales KPIs and average purchase value show that everything is ok. You lower your guard because you do not see any potential threats to your company.
However, the reality can be different from expectations. Probably, you do not see any occurring problems that may affect your team’s performance or even the financial results of the entire company. Therefore, you need professional sales analysis.
What about tracking sales KPIs in your company? Do you use sales dashboards that display them in your CRM system (Customer Relationship Management)? Do you know if every sales KPI in your organization is attainable? There are more questions that you should ask yourself. What do you know about your clients and their needs?
Precise sales analysis provides you with many answers to your questions.

As we have mentioned, sales analysis is essential to your company. However, a lot depends on gathering both qualitative and quantitative data on the sales process in your company.
If you use the right tool, you can analyze the entire sales cycle – from a meeting with a client to the closed deal and its sales value.
Salesbook is a tool that every sales manager can use to analyze sales. Moreover, it supports the everyday work of sales and marketing teams. It is a complete sales platform and analytical tool. It gathers data when a sales rep is in a meeting with a customer. Data are automatically sent to a system that can generate reports on crucial areas of sales.

Thanks to this, a sales rep does not have to make notes or fill in Excel tables in a hurry.
We can say that a typical sales cycle consists of the following elements:
In Salesbook, we have improved this process and created the SALESBOOK FORMULA by adding:
These elements allow you to do reliable sales analysis. You will read more about it in the next paragraph.
As we have mentioned, Salesboook allows you to analyze the sales cycle step by step. It is possible thanks to automation and collecting data during a meeting. Therefore, sales reps are bound to have all relevant data.
Take a closer look at a usual meeting with a customer that starts with the presentation of the offer.
“Great salespeople are relationship builders who provide value and help their customers win” – said Jeffrey Gitomer, one of the American business coaches.
Thanks to Salesbook, you gain knowledge not only about the number or places of meetings but also about sales reps’ methods that are the most effective.
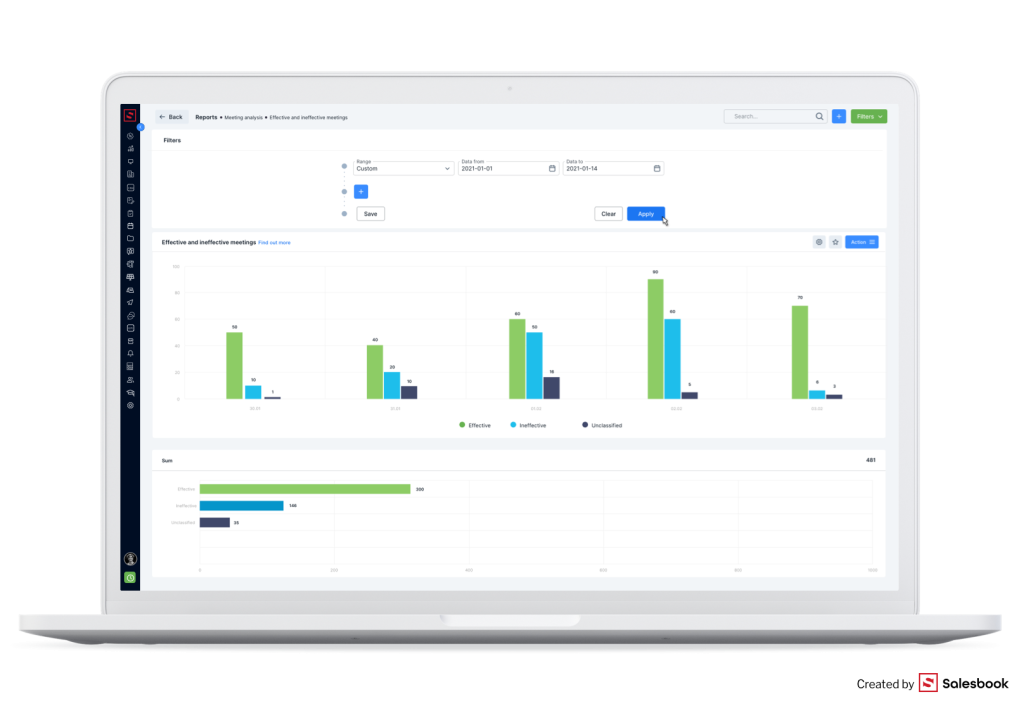
What can you know from reports on sales meetings?
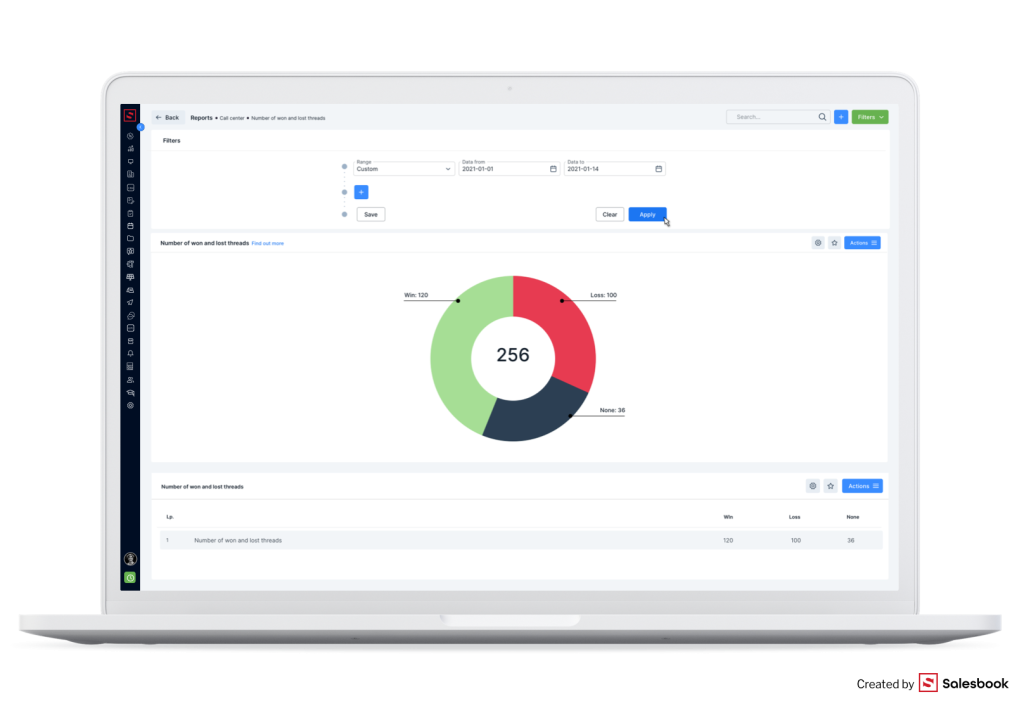
If you run your business in the Call Center industry, you can plan and implement a campaign with Salesbook. After its implementation, you can also analyze its results.
What can you analyze?
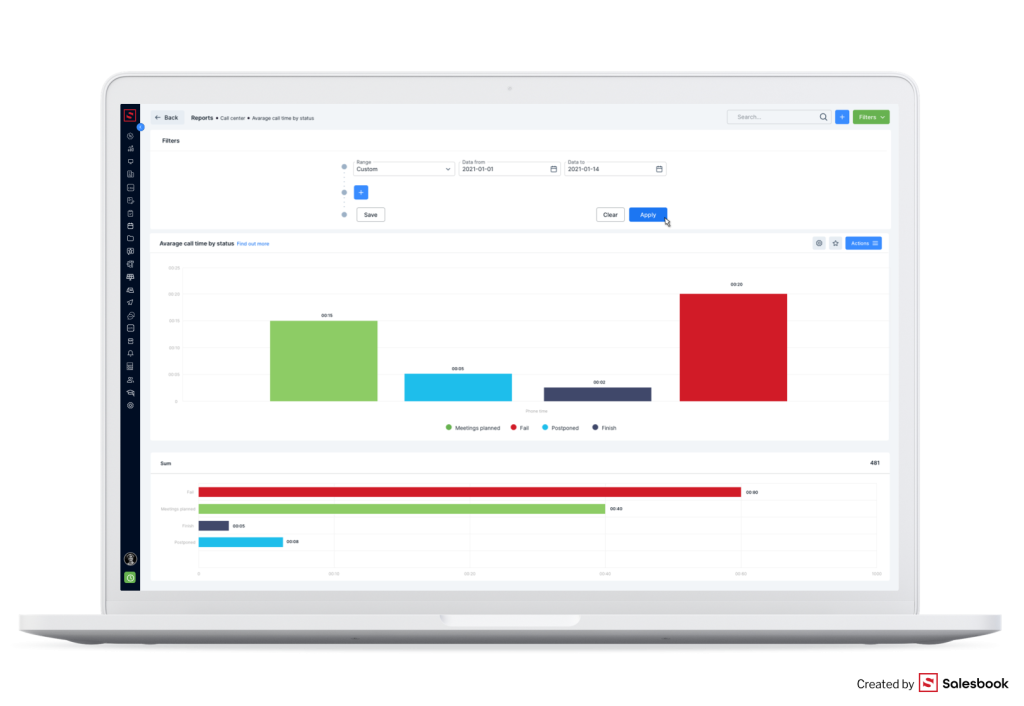
We have mentioned that sales meetings consist of the offer presentation and customer needs analysis. If a salesperson uses Salesbook, all data are automatically sent to the system. As a result, you can analyze every meeting step by step, and optimize it.
You can find out about:
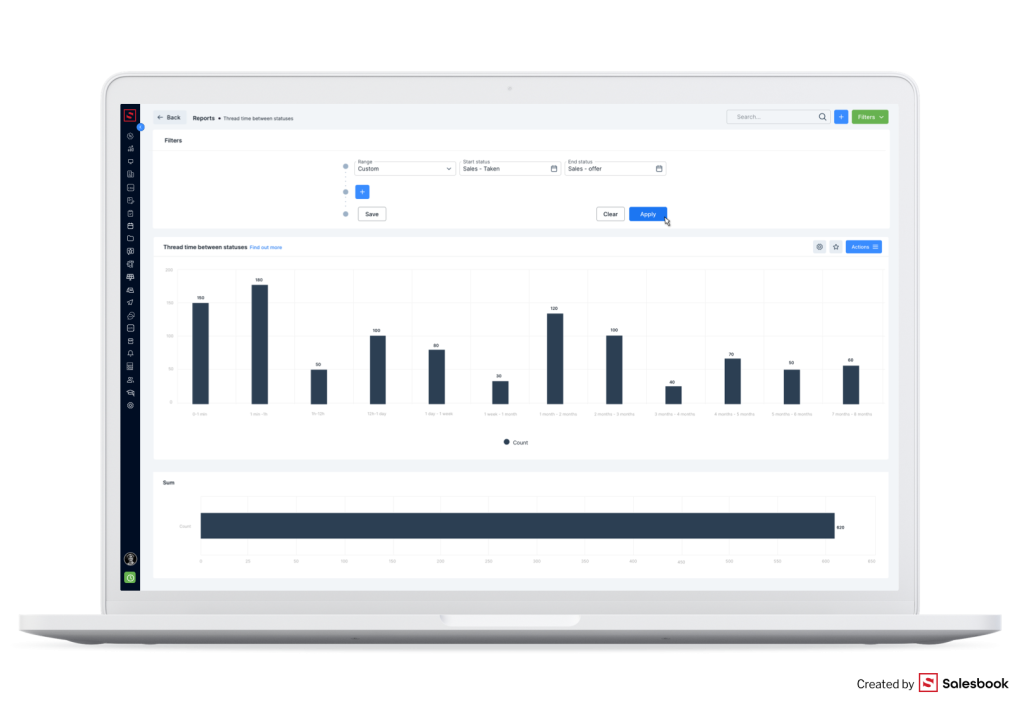
Sales are about being outstanding and giving your customers the best offer. If you analyze your sales with Salesbook, you know which elements are the most effective.
What can you know about sales of your products?
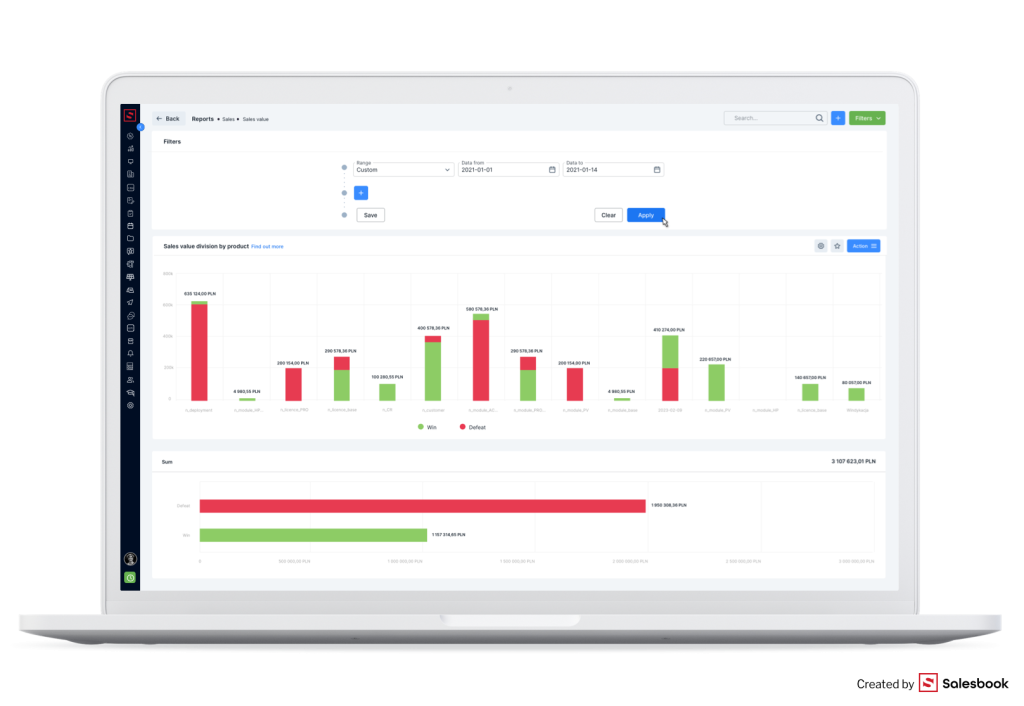
A sales value is another factor that you need to take into account during doing analysis.
If you use Salesbook, you can analyze your sales growth and:
As we have mentioned, KPIs for sales departments are necessary because they help measure the effectiveness of particular activities, and they are used to analyze sales. In Salesbook we have created the KPI module that allows you to define them precisely. Thanks to it, you have the exact data about every sales KPI you set.
What can you know about sales KPIs?
Thanks to sales forecast analysis, you will know the relationship between present sales value and your future goals.
What will you know using Salesbook?
Signing a contract is another element important to track and analyze. Thanks to analysis, you can monitor how many new contracts your company has gained or lost.

What can you analyze?
Summary
Salesbook is an effective tool for analyzing sales that has been chosen by many companies. Thanks to automation, you can be certain that you will have complete sales data and not omit any information.
Try our free demo to check Salesbook’s opportunities.

Any questions? Feel free to contact us.
+44 203 807 0179
Our Customer Success Team is available from Mon. to Fri. 9am - 5pm CET.
We support inquiries, processes of configuration and use of Salesbook app, as well as billing and technical issues.
